Live Cattle Contracts - How To Invest In Live Cattle? [Guide]
There are many futures contracts on the capital market. As a rule, investors know the most liquid instruments like futures on indexes, oil or stocks of companies. However, there are many more. Some are not very popular instruments for speculation and are usually used not for speculative but for hedging transactions. In today's text, we will present what are futures contracts on Live Cattle. We invite you to read!
READ: How to invest in food? ETN, ETF, REIT [Guide]
Live Cattle Contracts
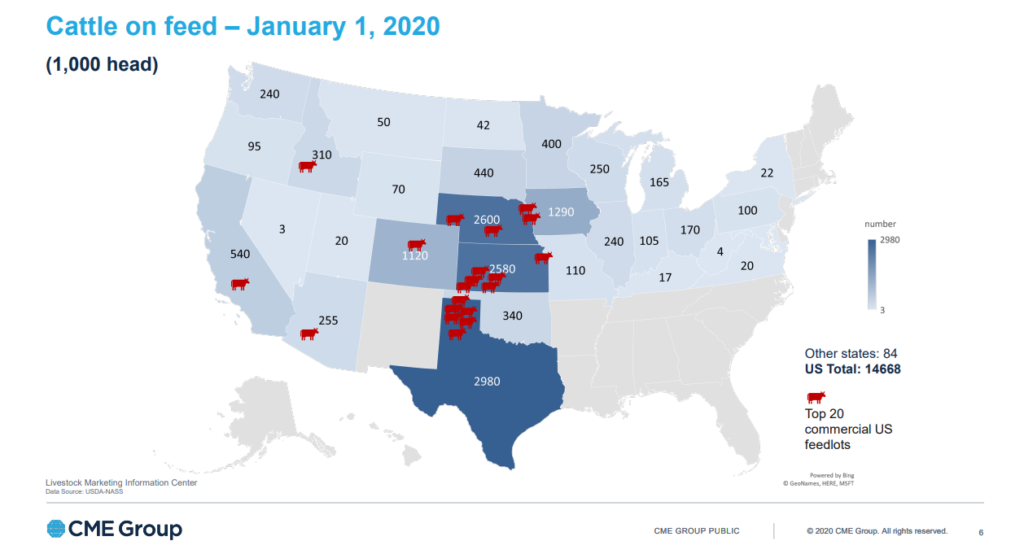
Although futures contracts in modern form have been known since the 1964th century, live cattle futures began to be available on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) only at the end of XNUMX. In the United States, more than half of the cattle are raised in three states: Texas, Kansas, and Nebraska.
Contract specifications
Each live cattle futures is for cattle weighing 40 pounds, which is approximately 000 tonnes. Contracts are cleared in US dollars with a minimum price fluctuation of $ 18 per pound. This means the minimum tick is worth $ 0,00025.
Futures contracts are settled in the following months:
- Luty
- Kwiecień
- Czerwiec
- August
- October
- December
Contracts are settled in the commodity. This means that if the investor has not closed the contract before it expires, he will be forced to sell or buy live cattle.
Responsibilities of the supplier and recipient
The owner of the short side of the contract (futures sale) at the time of delivery is compelled to fulfill the following conditions. These include, for example:
- Have a certificate that the cattle were born and raised in the United States,
- Cattle must be kept in pens, sorted and ready for presentation to the USDA representative.
Failure to meet the condition for loading cattle carries a fine of 3 cents per pound per day. There is a penalty of one and a half cents per pound per day if they are not sorted properly or are slowed down.
One contract equals £ 40, which is 000% of the cattle "Choice"and 35% "Select". What does this mean exactly? The USDA (US Department of Agriculture) divides beef into three types:
- Premium
- Choice
- Select
Beef choice it is of high quality but less marbling than beef type Prime . In turn, beef select it is more uniform and is usually leaner than the other two types of beef.
In addition, the permissible weight for steers is from 1050 to 1550 pounds, and for heifers between 1050 and 1350 pounds.
The recipient's obligations are much simpler. He "only" has to pick up the goods and arrange for them to be transported. If the recipient is unable to pick up the goods ordered or delays picking up, they will be subject to a fine of 3 cents per pound per day. The penalty is imposed by the USDA.
Turnover on the futures market
Looking at the live cattle futures market, most of the trading focuses on the June, August and October series, the expiry dates closest to the publication date of this article.
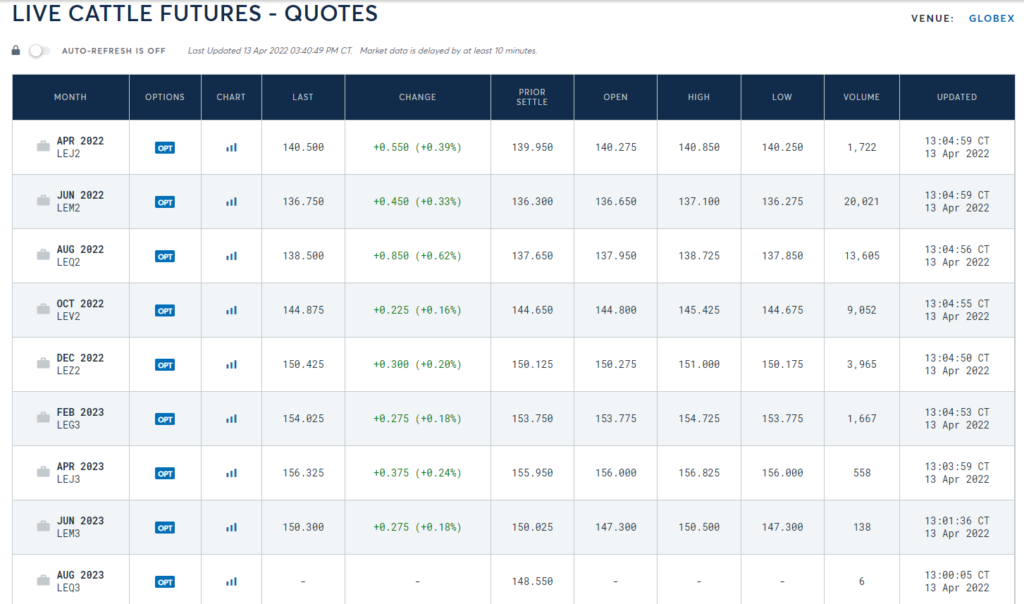
Source: CME Group
As you can see in the chart below, there is a trace of trading in series with a very long time-to-expiry. It grows with the approach of the contract implementation period. However, if there are only a few weeks left until the contract expires, there is a slow decline in trading due to contract rollover. In this situation, speculators switch to longer-term contracts to close the position before the derivative physical settlement.
Speculation and hedging on live cattle contracts
As you might guess, there are two groups of participants in this futures market. These are speculators and investors using futures contracts to hedge their operating activities. Speculators try to predict which direction of the price of the underlying instrument. This type of market participant is needed in the futures market because it ensures the liquidity of trading.
The second group are the so-called hedger's, that is, market participants who use futures contracts to hedge their position. One of the basic solutions is the use of the so-called "Lock-in"that is, securing the sale or purchase price in the future. This reduces the risk of running a business, but at the expense of exposing yourself to the risk of selling cattle too cheaply or buying at a much higher price than the market price.
Hedging
Cattle Futures can also be used as part of a hedging transaction. A farmer who does not use price hedging is actually a speculator as he is uncertain about the price of cattle in a few months' time. The breeder has to bear the costs of feed, labor and livestock keeping, but there is uncertainty about the selling prices of the cattle. This creates a risk that breeding, e.g. due to a drop in prices, will be more expensive than the market price. Live cattle futures can be used to remedy this.
An example is the sale of live cattle futures. In such a situation, the holder of the short commits to selling the cattle at a predetermined price. It is therefore a good solution for a cattle producer who wants to sell his product to a slaughterhouse but is concerned about the market price in a few months. Thanks to this, it can more accurately estimate the profitability of cattle breeding. If the market price of cattle increases, the breeder will suffer a loss on the hedging transaction after closing the hedging transaction. In the event that the cattle price drops, the breeder will cover the loss on the spot market through the profit of the hedging transaction.
Another example is buying live cattle futures. In such a situation, the holder of the long position undertakes to buy the cattle at a predetermined price. It is therefore a good solution for slaughterhouse owners who wish to secure the cost of the "raw material". In such a situation, the holder of a long position is protected against the increase in the price of cattle on the spot market. This allows you to better estimate production costs. Of course, if the cattle market price drops, the futures contract will generate a loss. This will cause the purchase costs to be higher than in the absence of the hedging transaction.
How to Invest in Live Cattle - CFD Brokers
A more affordable alternative for individual investors, whose aim is merely to speculate, are CFDs available from Forex brokers. In addition to significantly lower margin requirements, the trader does not risk having to "pick up" the live cattle when his contract expires. Below is a list of offers of selected brokers offering favorable conditions for trading on live cattle (CFD) instruments.
| Broker |  |
 |
 |
| End | Poland | Cyprus * | Denmark |
| Live Cattle symbol | CATTLES | LE / Live cattle | CATTLES |
| Min. Deposit | PLN 0 (recommended min. PLN 2000 or USD 500, EUR) |
PLN 500 | PLN 0 / EUR 0 / USD 0 |
| Min. Lot value | price * 400 USD | - | b / d |
| Commission | - | - | - |
| Platform | xStation | Plus500 platform | SaxoTrader Pro Saxo Trader Go |
* PLUS500 CY offer
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. From 72% to 89% of retail investor accounts record monetary losses as a result of trading CFDs. Think about whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford the high risk of losing your money.























![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)



![Live Cattle Contracts - How To Invest In Live Cattle? [Guide] live cattle contracts](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/kontrakty-live-cattle.jpg?v=1650011976)


![Live Cattle Contracts - How To Invest In Live Cattle? [Guide] Yield Guild Games ygg cryptocurrency](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Yield-Guild-Games-ygg-kryptowaluta-102x65.jpg?v=1649942284)
![Live Cattle Contracts - How To Invest In Live Cattle? [Guide] EURUSD parity](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/eurusd-102x65.jpg?v=1576771007)









