Japan - between tradition and modernity (part I)
Japan - the Land of the Rising Sun entered the family of industrialized countries quite late, because it was not until the second half of the 90th century. The Meji Revolution led to "Westernization with Japanese characteristics." Rapid industrialization and rapid adaptation of new technologies meant that Japan very quickly eliminated technological backwardness. Already at the end of the XNUMXs, Japan won the war with China.
However, the real shock was caused by Japan's victory in the war with Tsarist Russia in 1904-1905 (the famous battles of Tsushima and Mukden). As a result, the myth of "undefeated Europeans" began to collapse in Asia and it was the beginning of the end of Europe's domination in the Asian region. Until 1947, the Japanese Empire pursued an aggressive foreign policy. It waged wars with China, the United States, Great Britain, France, the Netherlands and the USSR. The defeats in World War II shattered the ambitions of a great power, but at the same time were the foundations for future economic success.
Japan in 1945 was economically devastated. It is estimated that as a result of bombing raids and broken production chains, industrial production was only 30% of the pre-war level. Zaibatsu (large banking and industrial groups) were banned and until 1952 Japan was occupied by American troops. After the outbreak of the war in Korea, there was a return to rapid economic growth. The country developed export-oriented production. There has also been a re-formation of industrial groups linked to banks.
A characteristic feature in Japan was the creation of Keiretsu, i.e. multi-industry alliances that were related to each other as a result of cross-links. The focal point in Keiretsu was the financing tank. The largest Keiretsu were: Mitsubishi, Mitsui, Sumitomo, Sanwa, Dai-Ichi Kangyo.
Due to the dynamic development of Japan, in the 70s it was the third largest economy in the world (behind the USA and the USSR). The rapid economic development meant that there were more and more voices that Japan was overtaking the world's largest economy - the United States. The undervalued exchange rate of the Japanese yen supported exports, and technologically advanced products (electronics) accounted for a significant share of it. After the Plaza Accord agreement, Japan agreed to strengthen the Japanese yen against the US dollar. The breakthrough moment was the bursting of the bubble in the real estate and equity markets in Japan. As a result, there has been a "lost decade". At the same time, the aging of the population has extinguished the demographic dividend. Lowering interest rates, asset purchases and increasing government debt did not lead to higher GDP growth and inflation. Abenomics introduced in 2012 was also moderately successful.
Japan, despite slow economic growth, is one of the most developed countries in Asia and the Pacific (in terms of GDP per capita PPP). Japan is also one of the largest economies in the world and a leading exporter. There are still many companies that specialize in the production of electronics in this country.
In recent years, Japan has signed free trade agreements with the European Union, as well as Great Britain and the United States. In 2020, Japan became a member of the RCEP, which includes fifteen Asia-Pacific countries.
Country development indicators
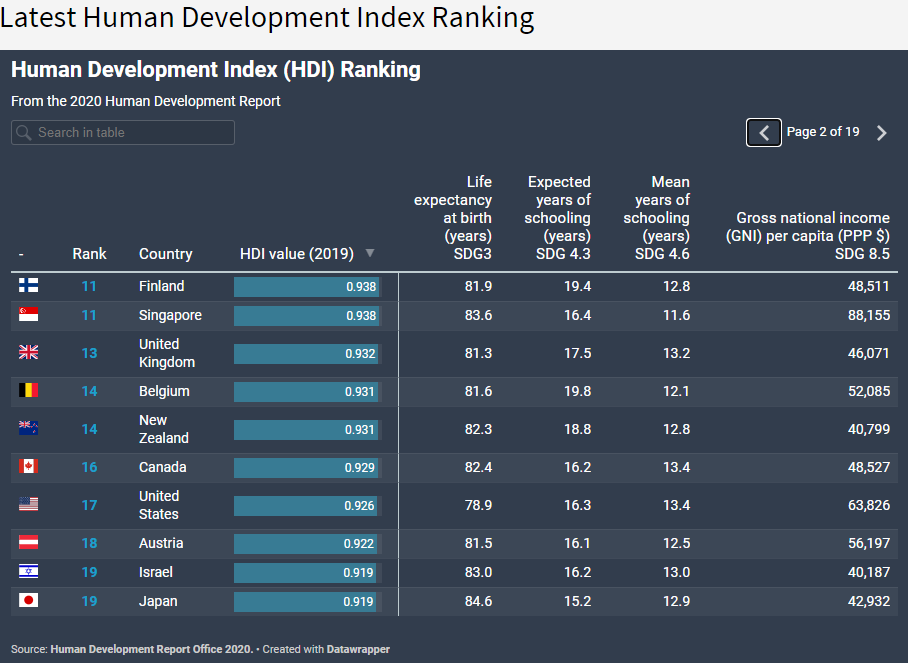
Japan is one of the most developed countries in Asia and the Pacific. It is also visible in the HDI (Human Developmet Index). The index assesses countries in terms of: expected quality of life, quality of education, and national income per capita. In 2020, Japan was tied for 19 with Israel. Slightly lower than the United States (17), but higher than South Korea (23) and France (26).
Japan does quite well in the ranking Corruption Perceptions Index (Corruption Perception Index) created by Transparency International. The Country of the Rising Sun in 2020 scored 74 points, which placed the country in 19th place. Japan was ahead of Poland (45), Chile (25) and South Korea (33). On the other hand, transparency is less than in the Nordic countries or Germany (9)
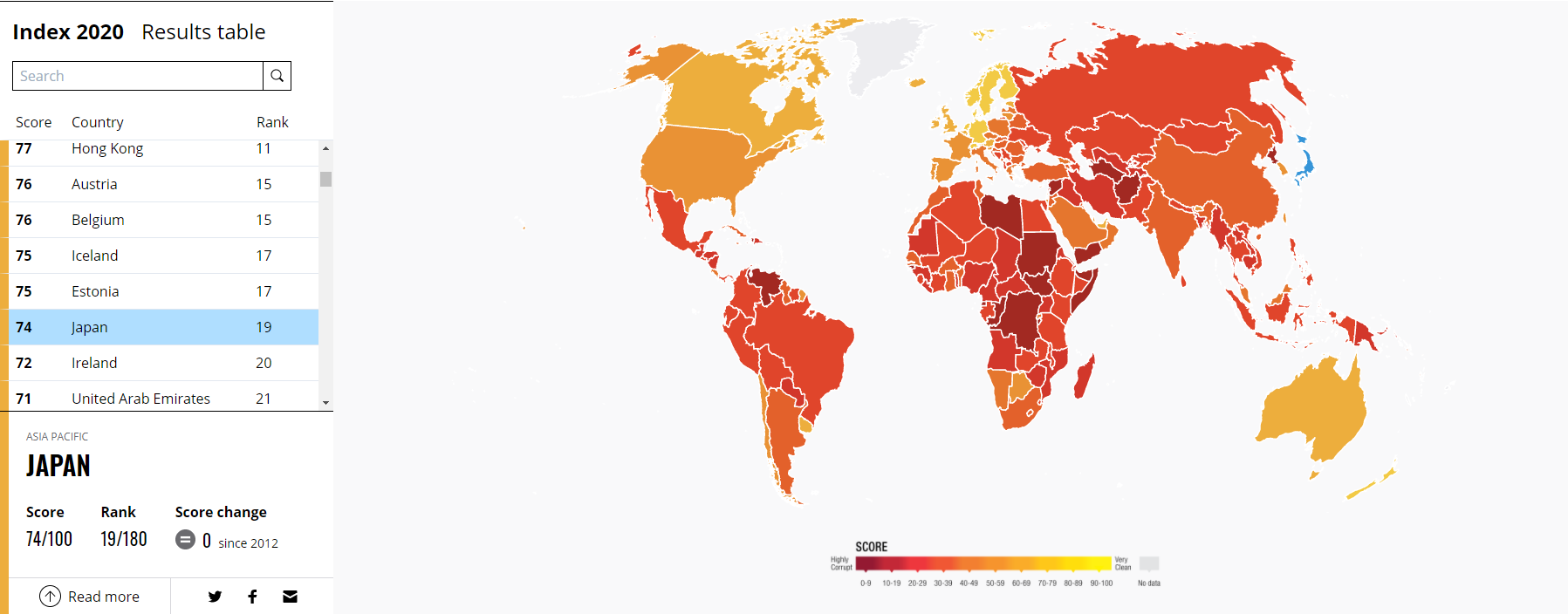
Source: transparecy.org
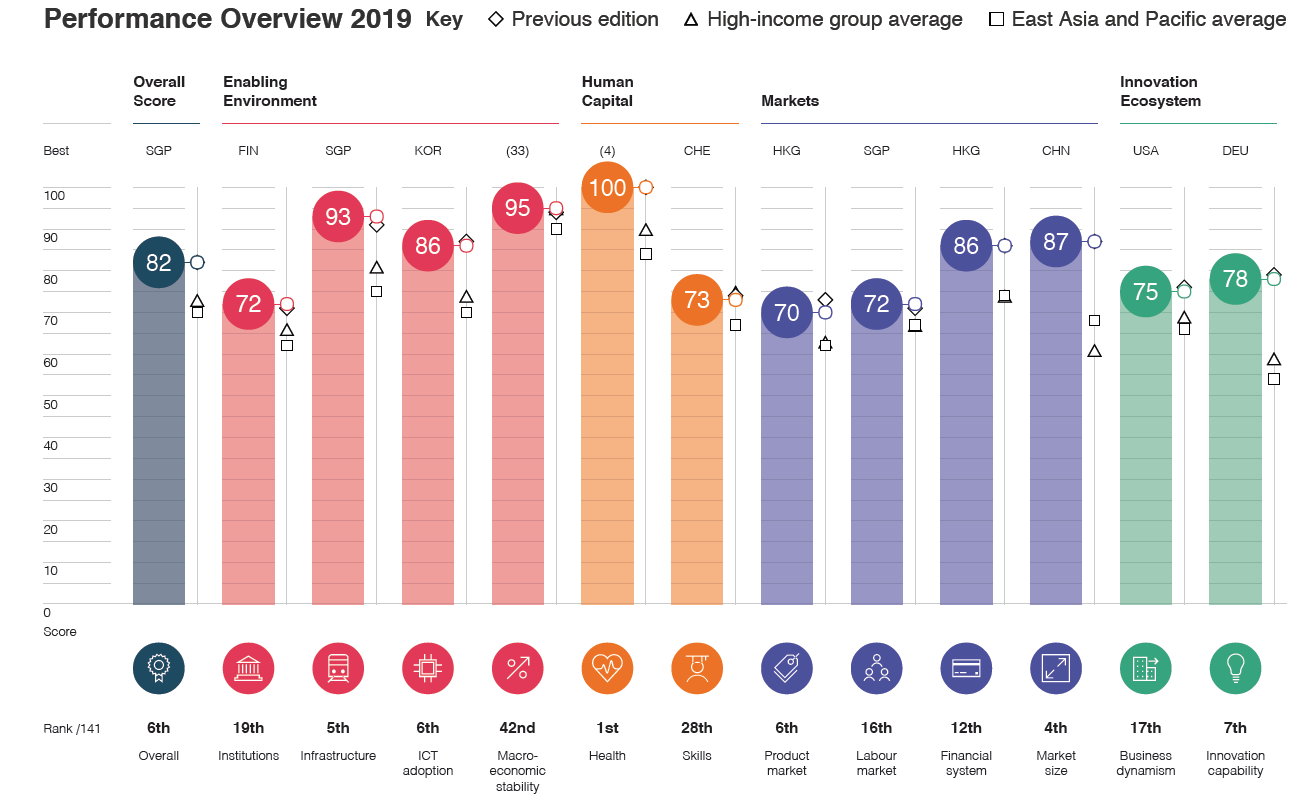
In the case of the competitiveness index Global Competitiveness Index Japan is already doing better than the CPI. At the end of 2019, the country was in the 6th position. The Land of the Rising Sun does very well in terms of health protection (1), market size (4), infrastructure (5), and the adoption of new technologies (6). Macroeconomic stability (42), institutions (19) and the labor market (16) fare worse.
In the case of infrastructure, the efficiency of the railway market is very good, with the ranking at 6,8 on a 7-point scale. As a result, Japan was classified as the country with the best railway in the world.
Japan fares much worse in the digital skills of the active population (58th place) and the ease of finding a highly qualified employee (54th place in the world). Learning critical thinking at school is also not very good (87th place).
The overall competitiveness index places Japan between Switzerland (5) and Germany (7). In the Asia-Pacific region, Japan fares worse than Singapore (1) and Hong Kong (3). On the other hand, Japan performs better in this index than other Asian tigers: Taiwan (12) and South Korea (13).
It's also worth remembering that Japan is a country of moderate inequality. This is clearly seen in the Gini index, which determines income inequality. It takes values from 0 to 1. The higher the index, the greater the stratification in the society. In the case of Japan, the Gini coefficient was 0,321 in 2019 according to the World Bank. Slightly higher than in the case of Poland (0,297), but less than in Brazil (0,539).
Japanese yen (JPY)
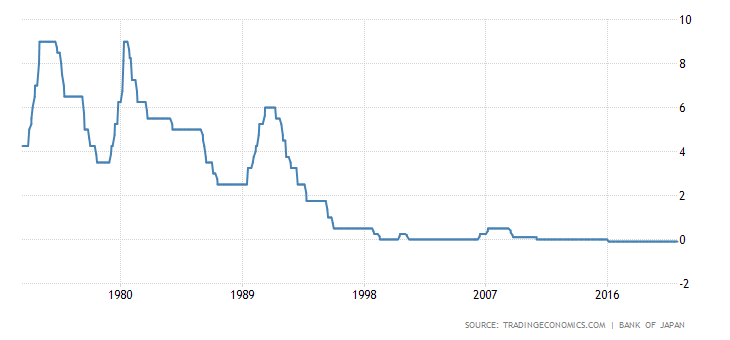
Between 1949 and 1971 the Japanese yen was pegged to the US dollar ($ 1- 360 JPY). After the agreement at the Plaza Hotel, the Japanese yen appreciated against the dollar. In 1985, the exchange rate was 239 yen to the dollar. After 3 years, the yen strengthened to the level of 128. The first peak of the yen's appreciation was in 1995 when the USD / JPY exchange rate reached 80.
The Japanese yen is one of the safe-haven currencies. As a result, during market turmoil, investors tend to sell the currencies of developing countries and place their funds in currencies such as the Japanese yen. This usually causes its appreciation. Monetary policy is led by Bank of Japan (BoJ). In recent years, the central bank has been known to pursue a loose monetary policy.
Interest rates - monetary policy
The fight against the economic slowdown, deflation and the aging demographic structure resulted in a significant reduction in interest rates in the 90s. At the end of the 0th century (with some breaks) it remained at around 0,1%. Currently, the interest rate is negative (-XNUMX%).
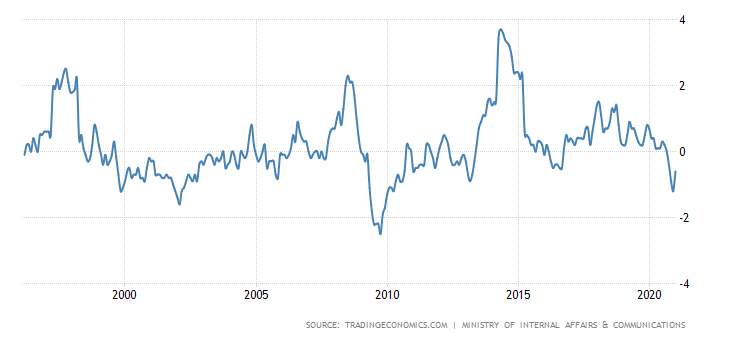
Japan has struggled to stimulate inflation over the past 20 years. Very often a country falls into periods of deflation. Only twice in the twenty-first century did inflation exceed the level of 2%. However, these were brief inflationary episodes. They were followed very quickly by a return to deflation or moderate inflation.
Economic development over the years
Japan has one of the largest economies in the world. According to data World Bank in 2019, the Japanese economy was the third largest in the world in terms of GDP ($ 5 billion). This meant less than 081% of the global GDP. Taking into account the purchasing power parity, Japan was ranked 5,78th in the world, between India (4rd place) and Germany (3).
Japan's economic growth has been moderate over the past 28 years. Between 1991 and 2019, GDP growth in purchasing power parity increased by 2,73% annually. The world grew at a slightly faster pace. This resulted in a decline in the share of the Japanese economy in world GDP, which fell from 8,4% to 4,1%.
The reason was, among others "Lost decade", which resulted from the low GDP growth rate, which caused, inter alia, the bursting of the real estate bubble at the turn of the 80s and 90s. At the same time, the maintenance of loose monetary policy and the links between companies (Keiretsu) led to the keeping of many "zombie companies" alive. This, in turn, is beneficial for workers on the one hand (keeping unemployment low), but it results in a misallocation of resources in the economy (which inhibits growth).
Below is a compilation of the World Bank.
|
GDP (PPP) |
1991 |
2005 |
2010 |
2019 |
|
Japan |
$ 2 billion |
$ 4 billion |
$ 4 billion |
$ 5 billion |
|
World |
$ 30 billion |
$ 66 billion |
$ 89 billion |
$ 135 billion |
|
% share of world GDP |
8,36% |
6,11% |
5,01% |
4,05% |
Source: own study
The table below shows that the years 1991-2019 did not belong to the "golden age" of the Land of the Rising Sun. Japan did not manage to catch up with the United States, it even regressed. At the same time, Japan has caught up with another economy in the region in terms of development. The fact that you can "run faster" is demonstrated by the example of South Korea, which caught up to overtake Japan in terms of GDP (PPP) per capita. Below is a compilation of the World Bank:
|
GDP (PPP) per person |
1991 |
2005 |
2010 |
2019 |
|
Japan |
20 849 $ |
31 663 $ |
34 986 $ |
$ 43 |
|
USA |
$ 24 |
$ 44 |
$ 48 |
$ 65 |
|
Poland |
$ 5 |
13 897 $ |
$ 21 |
$ 34 |
|
South bark |
9 471 $ |
25 187 $ |
31 748 $ |
44 011 $ |
|
World |
$ 5 |
$ 10 |
$ 12 |
$ 17 |
|
% US |
85,65% |
71,78% |
72,19% |
66,94% |
|
% South Korea |
220,14% |
125,71% |
110,20% |
99,05% |
Source: own study
In the case of Japan, the economy is based on services, where 68,7% of the Gross Domestic Product is produced. In turn, the industry is responsible for approximately 30,1% of the Gross Domestic Product. Japan is the largest car manufacturer in the world. It is in this country that companies such as Toyota, Nissan, Honda, Suzuki and Mazda have their headquarters. It is worth mentioning that Toyota is the largest car manufacturer in the world. The steel industry, which ranks second in the world, should also be mentioned. The electronic industry is very developed in the country. It is in this country that companies such as Canon, Casio, Hitachi, Nikon, Nintendo, Sony and Panasonic operate.
Unemployment rate
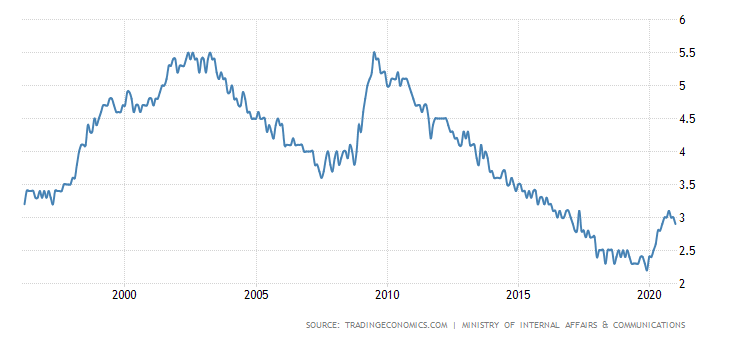
The Japanese economy is able to provide employment for the working-age population. Between 2010 and 2020, the unemployment rate dropped from 5,5% to 2,25%. During the COVID-19 epidemic, it rose slightly to 3%.
The low unemployment rate applies to both women and men. However, incl. due to cultural factors, the participation rate in the working age population differs according to gender. According to The Global Gender Gap Index 2020 for women participation rate was 69,8%. For men, this ratio was 85,8%. Therefore, you can see a significant difference in professional activation women and men. It is therefore not surprising that during the introduction of abenomics, apart from the slogans of labor market liberalization, the postulates of professional activation of women were hungry.
Despite the low unemployment rate for women (below 3%), the employment structure is different than for men. There is much more part-time work for women (36,7% of all female employees) than for men (11,5% of male employees). Women are usually employed in middle and lower level positions. Only 5% of management board positions in listed companies were filled by women.
It is therefore not surprising that The Global Gender Gap Index classified Japan in the Economic Participation and Opportunity category at just 115th place. For comparison, Poland was ranked 57th in this ranking, and the United States 26th. On the other hand, Japan fared better than South Korea (127).
Debt to GDP
Japan is the country with the highest level of sovereign debt to Gross Domestic Products. In 2020, this ratio exceeded 260% (as a result of stimulus packages). However, low interest rates, macroeconomic stability and a small percentage of debt held by foreign investors meant that there are no problems with debt service so far.
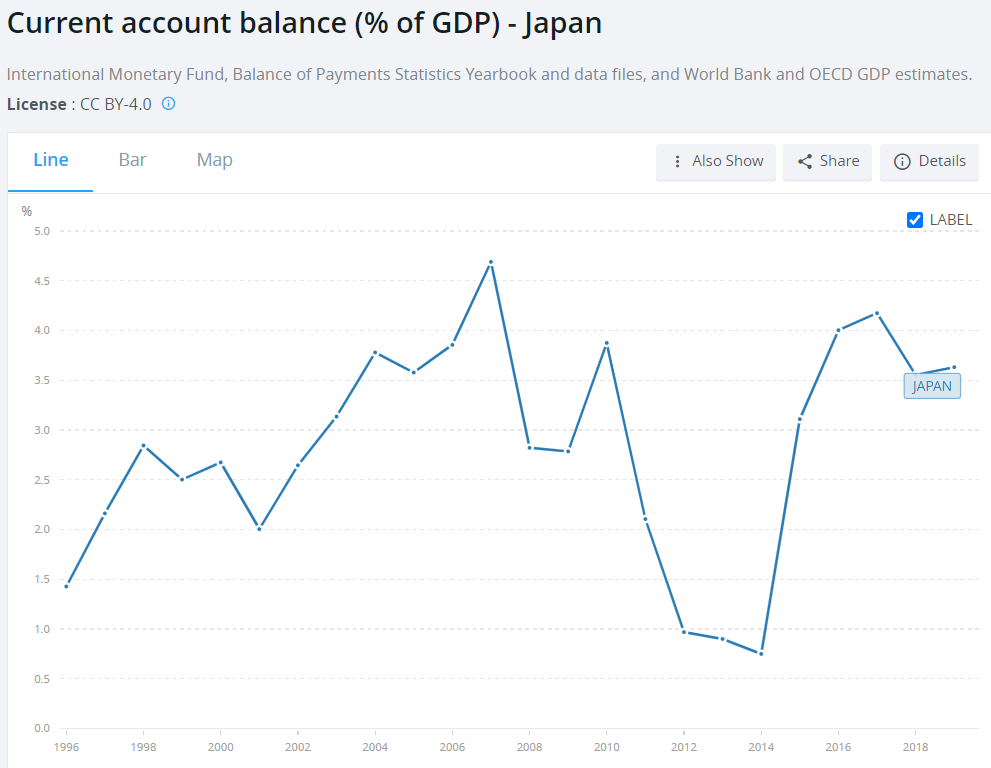
Due to the stable macroeconomic situation, the current account surplus and the lack of problems with the debt rollover, Japan enjoys good ratings. The S&P agency set the rating for government debt at A +, while Fitch A.
Japan has a significant current account surplus, which proves that the Land of the Rising Sun is a capital exporter. As a result, Japan is less sensitive to "external shocks" that cause capital outflows.
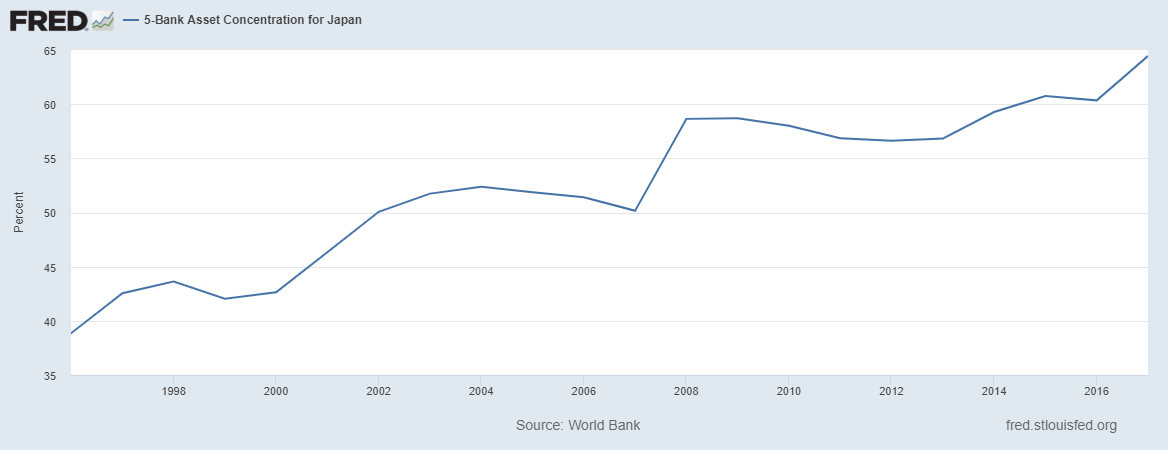
Banking sector
The Japanese banking sector is dominated by the "big five" which include Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group, Mizuho Financial Group, Japan Post Bank and Norinchukin Bank. According to data collected by the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis "big five" controls more than 64% of assets.
World Trade
The Japanese economy is much less export-oriented than the world economy. The impact of exports is much lower than that of South Korea (40%) or Vietnam (106%). Below is a comparison of selected countries:
|
Exports of goods and services as% of GDP |
1991 |
2005 |
2010 |
2019 |
|
Japan |
9,78% |
14,01% |
15,04% |
18,52% |
|
Germany |
23,67% |
38,06% |
42,56% |
46,97% |
|
USA |
9,66% |
10,01% |
12,32% |
11,72% |
|
South Korea |
23,78% |
35,28% |
47,10% |
39,95% |
|
China |
14,49% |
33,83% |
27,18% |
18,41% |
|
Vietnam |
30,91% |
63,70% |
72,00% |
106,8% |
|
World |
19,20% |
28,59% |
28,92% |
30,62% |
Source: World Bank
A good definition of a position on the trade map is the trade openness index, which determines the relationship between trade turnover (exports and imports) and a country's GDP. The higher the index, the more international trade plays a greater role in the country's economy. In the case of Japan, it is clear that it is an economy much less dependent on trade than the Vietnamese or Korean economies.
|
Trade as% of GDP |
1991 |
2005 |
2010 |
2019 |
|
Japan |
18,07% |
26,52% |
28,61% |
36,82% |
|
Germany |
47,82% |
70,92% |
79,87% |
88,09% |
|
USA |
19,79% |
25,56% |
28,06% |
26,39% |
|
South Korea |
49,83% |
68,33% |
91,40% |
77,00% |
|
China |
25,59% |
62,21% |
50,72% |
35,68% |
|
Vietnam |
66,95% |
130,72% |
152,22% |
210,40% |
|
World |
38,53% |
56,09% |
57,03% |
60,40% |
Source: World Bank
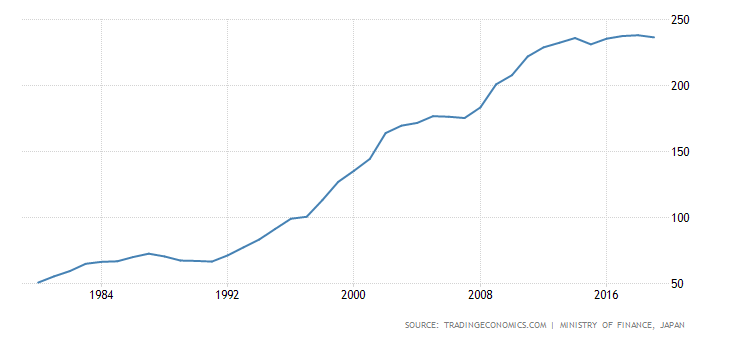
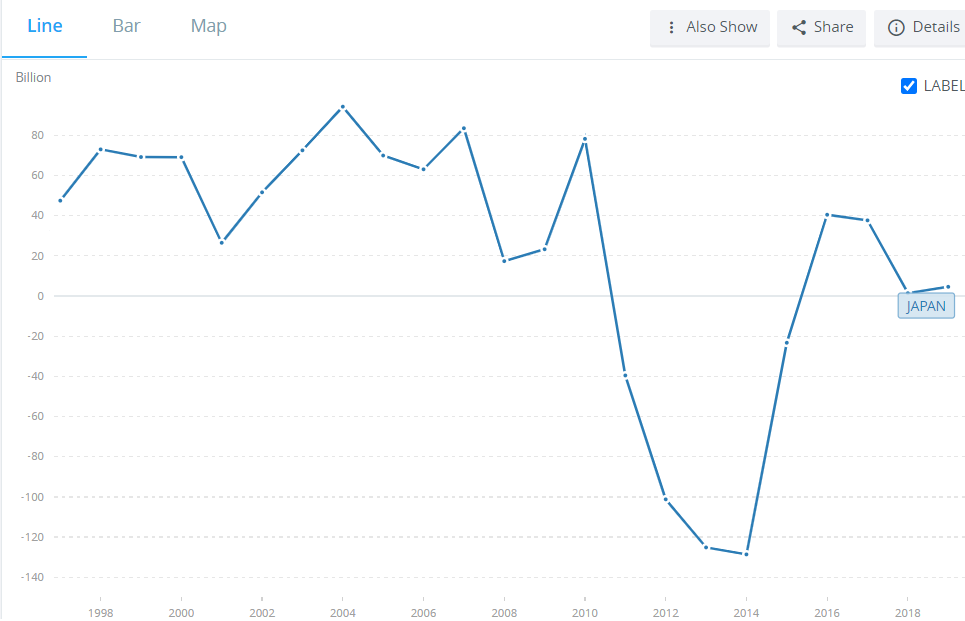
Japan is one of the largest exporters in the world. According to data collected by the World Bank, Japan was classified in 4th place. The value of exports was estimated at $ 905 billion. This is more than exports from the United Kingdom, France or Russia. However, this is not a typical export-oriented economy. Over the past 25 years, Japan has generally recorded a trade surplus in goods and services.
Source: World Bank - Trade Balance
Japanese trade continues to be concentrated in Asia and the US market. The largest trading partners are the United States and China. This applies to both export and import.
The exports are dominated by car parts and cars (21,1%). It is followed by industrial equipment (19,4%) and electronic devices (14,6%).
Where does Mexican export go - the main partners
Biggest buyers Mexican goods there are two of the world's largest economies. The largest part of exports goes to the United States ($ 140,4 billion). The next main direction of trade is China ($ 134,6 billion). The main Asian markets are other key export destinations.
|
Place |
End |
Turnover value (billion $) |
|
1 |
United States |
140,4 |
|
2 |
China |
134,7 |
|
3 |
South Korea |
46,3 |
|
4 |
Hong Kong |
33,6 |
|
5 |
Tajlandia |
30,2 |
|
6 |
Germany |
20,2 |
|
7 |
Singapore |
20,2 |
|
8 |
Vietnam |
16,5 |
|
9 |
Australia |
14,5 |
|
10 |
Indonesia |
14,0 |
Source: UN Comtrade
Where does Japan import from - main partners
More than one fifth of imports come from China. Another major partner is the United States. Apart from countries in the East Asian region, hydrocarbon exporters (Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates) are important partners.
|
Place |
End |
Turnover value (billion $) |
|
1 |
China |
169,2 |
|
2 |
USA |
81,2 |
|
3 |
Australia |
45,5 |
|
4 |
South Korea |
29,6 |
|
5 |
Saudi Arabia |
27,6 |
|
6 |
United Arab Emirates |
26,2 |
|
7 |
Tajlandia |
25,4 |
|
8 |
Germany |
24,9 |
|
9 |
Vietnam |
22,5 |
|
10 |
Indonesia |
18,2 |
Source: UN Comtrade
Due to its scarce raw material resources, Japan imports a lot of hydrocarbons. It is therefore not surprising that hydrocarbons account for as much as 21,6% of imports. Other important import products were industrial equipment (9,8%) and electromechanical equipment (13,7%). It is also worth noting that metal ores account for over 3% of total imports.
Demography - a healthy demographic structure
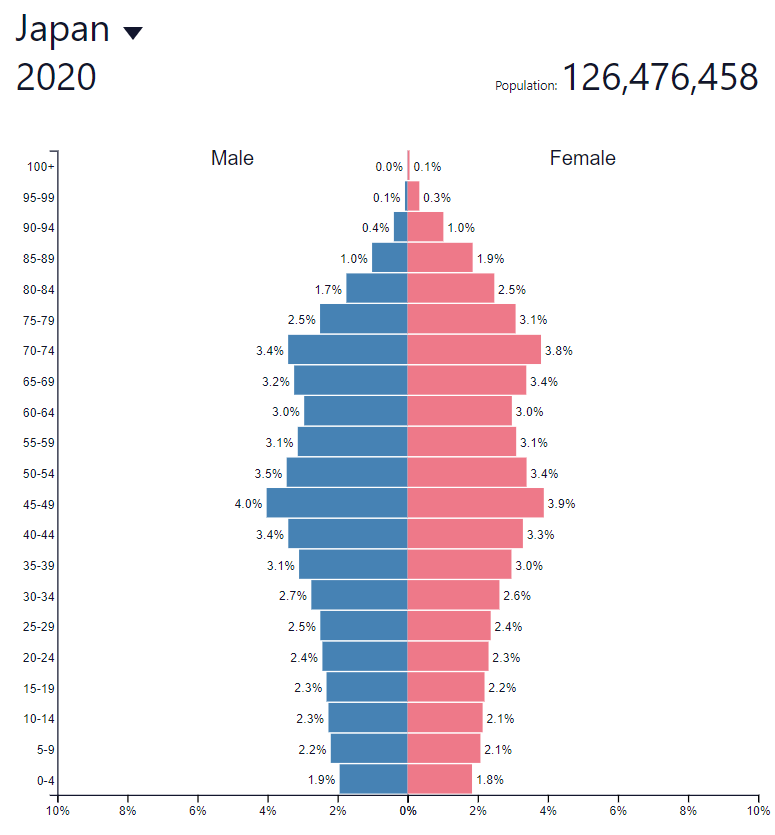
According to data from the United Nations, Japan in 2020 had a population of about 126,5 million. This means that it is one of the most populous countries on earth.
According to the United Nations, Japan's population will drop to 30 million over the next 105,8 years. Below is a comparison with the United States and South Korea. As a result of the population decline, Japan will not be able to benefit from the high proportion of its working age population in the total population. Demographic aging will have a negative impact on economic growth.
|
Country / Region |
2020 |
2050 |
CARG% |
|
Meksyk |
126,5 |
105,8 |
-0,60% |
|
United States |
331,0 |
379,4 |
+ 0,46 % |
|
South Korea |
51,3 |
46,8 |
-0,31% |
|
World |
7 794,8 |
9 735,0 |
+ 0,74 % |
Source: UN World Population Prospects 2019
Japan is a country with a high rate of urbanization. According to data collected by the CIA, over 91,7% of the population lives in cities. The largest economic center in Japan is the country's capital - Tokyo. According to the Japan Statistics Office, the city's population exceeds 9 million.
Japan's demographic structure heralds a continuing aging of the population. The low fertility rate (1,43) suggests that the demographic pyramid is expected to deteriorate in the next 30 years. Due to immigration difficulties, low fertility rates will not be "covered" by "letting" large numbers of immigrants into Japan (which would improve the demographic structure).
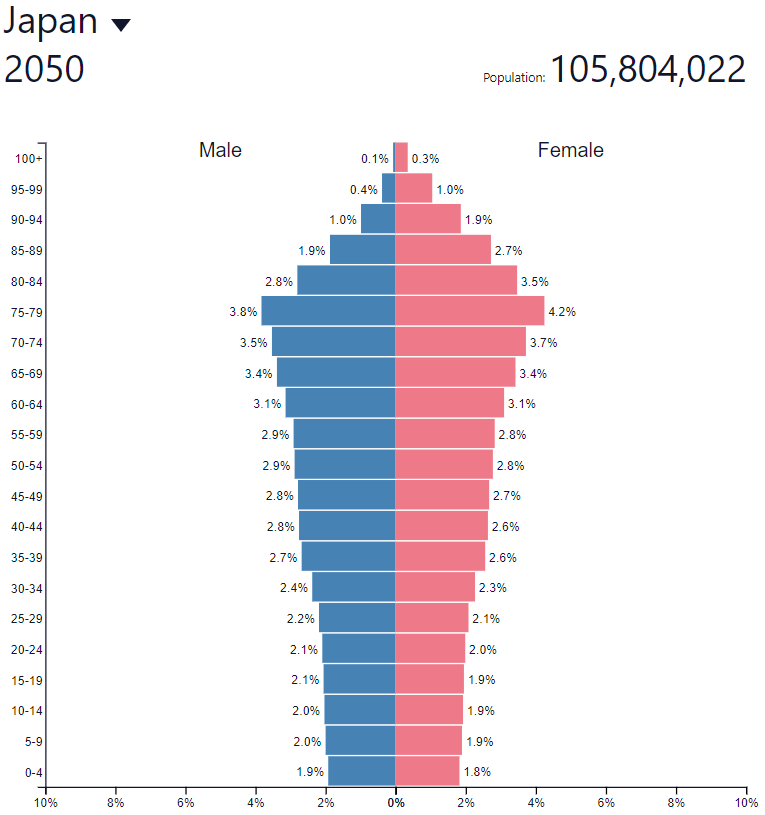
 This means that a significant increase in the demographic burden is to be expected. Old dependency ratio is 48,0%. It is an indicator that divides the number of people aged over 64 by the number of people of working age (15-64). 50 years ago, the rate was 10%.
This means that a significant increase in the demographic burden is to be expected. Old dependency ratio is 48,0%. It is an indicator that divides the number of people aged over 64 by the number of people of working age (15-64). 50 years ago, the rate was 10%.
Summation
Japan is one of the largest economies in the world. It has a well-developed automotive, steel, electronic and precision machinery industries. The country is closely related to its economies in terms of trade other Asian countries. The reason is the geographical proximity and the dynamic growth of this area. The main trading partners are still the United States and China.
The country of the Rising Sun is a country with a stable macroeconomic situation. Japan, however, is a developing country with minor corruption problems (according to Corruption Perceptions Index) and a high rate of gender inequality.
The country is in 19th place in terms of the HDI index. As a result of the bursting of the real estate bubble in the 90s, convergence with the US economy (PKP PPP per capita) stopped. Despite slow economic growth and high indebtedness, the yen is classified as a safe haven. Population decline and an aging population will be a problem to economic growth. However, it should be borne in mind that the rapid introduction of robotization may help increase productivity, which will "cover up" demographic problems. As early as 2017, Japan was at the forefront of "robotic" countries with 308 robots per 10 employees. For comparison, the US had an index of 000 and Switzerland 200. Despite your problems, it is worth having the Japanese market on the "investment radar".






















![Forex Club – Tax 9 – Settle tax on a foreign broker [Download the Application] Forex Club - Tax 9](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Forex-Club-Podatek-9-184x120.jpg?v=1709046278)
![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)