Contango - a slayer of long-term investors
Investing in the commodity market only seems simple at first glance. It's enough “buy low, wait and sell high”. However, futures trading is not as trivial as it may seem. One example is that many novice traders are not even aware of the existence of such effects as contagion i backwardation. Lack of understanding of these issues often results in making wrong investment decisions. The real nightmare for those who want to invest positionally on the futures market is contango. Due to its negative impact on the rates of return obtained, it can be called it “long-term investor slayer”. In this article, we will briefly explain what this phenomenon is and how it can be used in trading on the stock exchange. We invite you to read!
What is the contango effect?
At the very beginning, you need to explain what it is futures contract. In short, it is a derivative in which the buyer of the contract agrees to buy the underlying at a specified price. The contract is settled when it expires. In turn, the writer of the contract undertakes to sell the underlying instrument on the same terms as the other party to the contract.
Since the contract concerns a price from the future, we cannot be surprised when the forward price differs from the market price of a given commodity. Depending on a number of factors, the forward price may be higher or lower than the spot price. Of course, as the expiration date of a futures contract approaches, the futures price and the spot (market) price align.
The contango effect is a situation when the forward price paid by the buyer of the contract is higher than the market price. Another word for this situation is forwardation. Below is a classic example of contango in the livestock market. The longer the delivery period for a given commodity, the higher the forward price.
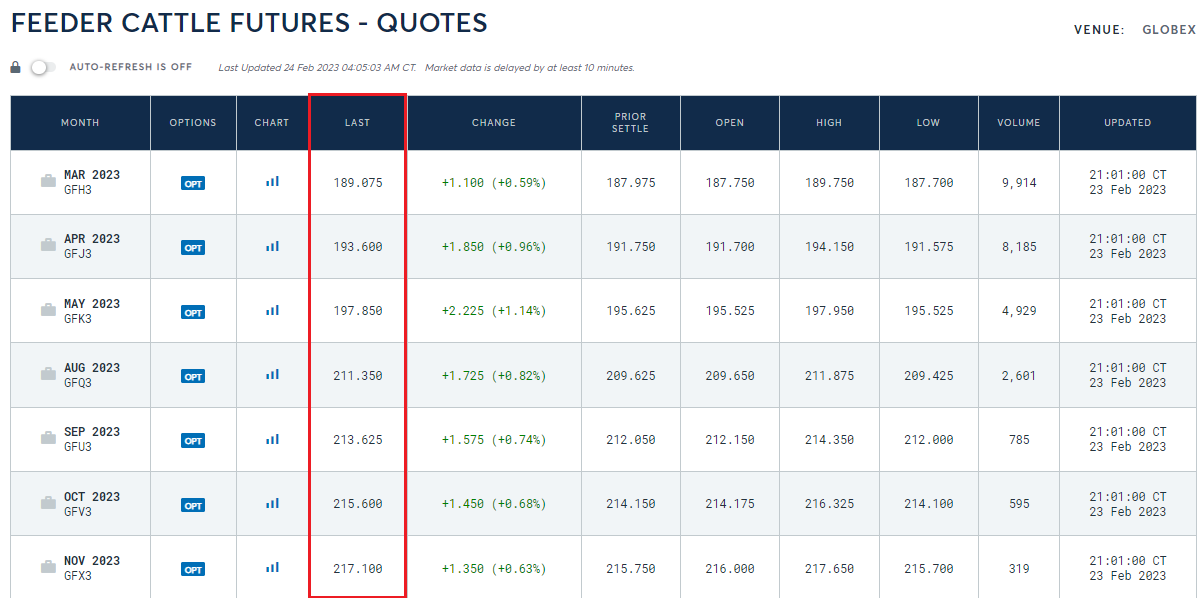
Source: CM extension
Because a futures contract is about the future- and this one is uncertain - the supplier of a given commodity must, at least theoretically, hedge against the risk of concluding a contract. For this reason, the so-called cost of carry. It includes the costs of interest, insurance and storage of the goods. If a given commodity is susceptible to "spoilage", this factor will also be taken into account in the futures contract. These factors are the “normal” components of contango. Most often, the contango is not more than a few percent (in periods of low interest rates, it is usually 1-2%).
Of course, the cost of carry does not apply to perishable goods. Such goods include fresh fruits and vegetables or fish. This is due to the fact that a different delivery date applies to a different product, because it is not suitable for storage without losing its properties. For example. fresh fruit in 3 months will no longer be fresh fruit. So in 3 months the futures contract will be for “other fruits”.
In turn, Petroleum has the same properties in 1 month as in 3 months (if stored under different conditions). And it is precisely this type of goods that the contango effect applies to.
There are three lines in the chart below. Dark blue means keeping the price in contango, in turn light blue this is price behavior in backwardation. Both lines go to redwhich is the spot price. The closer it is to the settlement of contracts, the smaller the difference between the spot price and the forward price. Based on this relationship, a number of strategies have been developed.
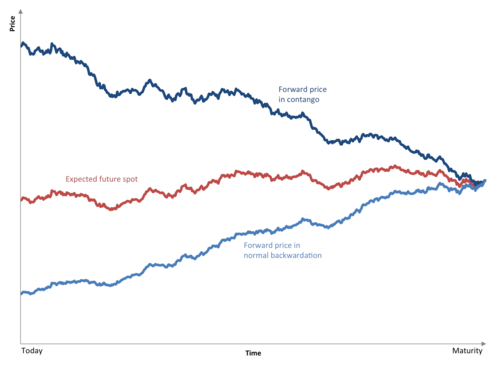
Source: wikipedia.org
Oil-storage strategy
There are situations when the contango is very large. The most obvious example is the frequent fluctuation of crude oil prices (e.g. over 50% of contangos have contracts with 5 months longer expiration dates in 2020).
READ: Oil price minus. Futures contracts lowest in history
In the 90s, a strategy was developed that allowed you to earn on the difference between the spot price and the forward price. The strategy was to buy crude oil at the market price and then store it for later sale at a higher price. Oil was stored on tankers, reservoirs and salt mines. Then, the investor waited for an increase in the futures price of contracts with a longer delivery period and opened a short position on these contracts. The strategy was used even by banks operating on the commodity market (Goldman SachsMorgan Stanley, Citigroup).
Arbitration
Arbitrage trading is about using the contango effect to make a risk-free profit. Thanks to the actions of arbitrageurs, there is usually not much difference between the futures price and the spot price. This is because too much contango can encourage investors to sell the futures contract longer strike price and buy the underlying asset at the spot price. If the cost of carry of the underlying asset purchased is less than the difference between the futures price and the spot price, the arbitrageur will generate a profit.
Spread trading
This is a strategy in which the investor assumes that the difference between the futures price and the spot price will be even greater. In such a situation, the trader takes a long position on the “further contract” and a short position on the future contract. The investor will make money if the spread actually widens. If the contango decreases slowly, the investor will generate a loss on the trade.
The impact of Contango on long-term strategies
Contango is not a problem for day-traders or short-term investors. However, it is an important consideration for long-term investors. For example, those who are unaware of the risk and invest in “commodity ETFs” have a problem. Some ETFs they do not physically replicate the benchmark but use futures contracts. They very often use the strategy of autorolling the contract. By purchasing a new series above the spot price, an ETF investor incurs a contango cost, which he is often unaware of. This cost is visible during the side market, when despite the fact that the ETF has not changed, the management costs and the contango effect make the rate of return on the ETF negative.
Summation
Contango is a situation when the forward price is higher than the market price. A large difference between the spot price and the forward price may cause the long-term trader who uses automatic position rollover to incur a “hidden cost” of the strategy. So it is the real “enemy” of long-term investors. Keep this in mind the next time you buy raw materials for the "long term".























![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)


















