CFTC - the guardian of the organized derivatives market
The CFTC, or Commodity Futures Trading Commission, is an independent agency of the United States government whose purpose is to regulate the American derivatives market. The CFTC can be divided into 5 main operational areas:
- DSIO (The Division of Swap Dealer and Intermediary Oversight) - supervises intermediaries in the derivative market (e.g. introducing brokers, swap dealers or Forex brokers)
- DCR (The Division of Clearing and Risk) - supervises, among others, clearing organizations
- DMO (The Division of Market Oversight) - overseeing the derivative market, trading practices, etc.
- DEO (The Division of Enforcement) - investigates and prosecutes alleged violations of CEA (Commodity Exchange Act) and CFTC
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) is an independent government agency that was founded in 1974 and replaced the CEA (Commodity Exchange Authority). The CFTC regulates the American derivatives market (e.g. futures, swaps and part of the options market). The Commodity Exchange Act requires from "Brokers" in the derivatives market registered with the CFTC. An intermediary is a person or institution that trades on a derivative market (futures, swap and options) on behalf of others.
The goal of the CFTC is to promote the integrity and resilience of the US derivatives market through appropriate regulation. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission employs over 700 people with branches in Chicago, Kansas City, New York and Washington. The institution's projected budget for the 2021 financial year is $ 304 million, an increase of approximately 7% over the year.
History of regulating the futures market
Regulation of commodity derivatives began in the 1936s with the entry into force of the Grain Futures Act, which was established by the Grain Futures Administration. The next step in regulating the derivatives market was the Commodity Exchange Act of 1974, which introduced federal regulations to the entire market of futures and commodity options that were traded on the organized market (stock exchange). The institution responsible for regulating this market was the Commodity Exchange Authority, which was part of the USDA (US Department of Agriculture). In XNUMX, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) took over the CEA powers.
The further increase in the rights of the CFTC came with the adoption of the Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000 by the American Congress. CFTC together with the SEC began to be responsible for the stock futures market. The new product was introduced to the market in November 2002.
The bursting of the real estate bubble in 2007-2009 exposed the US government to the risk of the network. The swap market was a particularly big problem. In 2010, the reform came into force Dodd Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. One of the changes introduced by "Dodd-Frank Act" was to extend the powers of the CFTC to regulate the swap market.
CFTC authorities
The CFTC also includes 5 commissioners who are appointed by the President of the United States for a five-year term. One of the commissioners is nominated to act as president.
The head of the CFTC is Heath P. Tarbert, who was appointed to the position in July 2019. His mandate will run until April 2024. HP Tarbet also has a voting member on the Financial Stability Supervisory Board (FSOC). He is also the vice chairman of the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO). Mr. Tarbert is also a holder of CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) and CPA (Certified Public Accountant) certificates. In his career, he worked, among others, as the director of The World Bank and in the Senate Committee on Banking, Housing and City Affairs.
It is also worth mentioning the other commissioners, which are:
- Brian D. Quintez - Nominated by President Donald Trump in May 2017.
- Rotin Behnam - Nominated by President Donald Trump in July 2017.
- Dawn DeBerry Stump - nominated by President Donald Trump in June 2017 for a 5-year term.
- Dan M. Berkovitz - nominated by President Donald Trump in April 2018 for a 5-year term.
Penalties imposed by the CFTC
The penalties imposed by the regulator are really different. From several hundred thousand dollars to hundreds of millions of dollars. A case can be given as an example of a minor penalty Gain Capital UK Limited. The London branch of the owner of brands such as Forex.com or City Index was fined $ 250. The reason was breaking the US law, which forbade operating on the forex market in the territory of the United States without registration with the CFTC, SEC or banking supervision. Gain Capital accepted US investors without registering with the relevant regulatory authorities.
Sometimes the penalties can be really high. The biggest penalty ever issued by the CFTC was the case of unfair futures practices by the US bank JP Morgan. The verdict in this case was issued in September 2020. The bank has been manipulating the derivatives market for over 8 years. One of the unfair practices was spoofing, which involved manipulating the order book. A trader looking to sell a large bundle of contracts at a better price uses spoofing to raise the price. Initially, he places a visible large buy order on the spreadsheet, which is supposed to imply a strong demand. This encourages some traders to take long positions, which raises the quotation price. Then the placed large buy orders are pulled from the sheet. In the next step, the trader starts opening short positions using the higher price.
JP Morgan used this technique between 2008 and 2016, achieving multi-million dollar profits. Estimates were up to $ 250 million in profits per year from this practice. In September, the process was completed. The CFTC imposed a fine of $ 920 million. It was the highest penalty ever imposed by the CFTC on a derivative market participant.
By virtue of "Dodd-Frank Act" rewards for "Whistleblowers" from financial institutions. A whistleblower is a person who, seeing inappropriate behavior of his employer (financial institution), submits a notification of a suspected crime. According to the new rights, the whistleblower may be rewarded from 10-30% of the fine (the minimum penalty threshold for the award is over $ 1 million). The CFTC provides whistleblowers with anonymity. Sometimes the rewards are high. In 2018, one employee of an investment bank received a $ 30 million award. It was related to a settlement with one of the investment banks. Under it, the financial institution agreed to pay $ 367 million.
Read: $ 30 million Whistleblower whistleblower prize
COT reports (Commitments of Traders)
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) regulator is best known for being published weekly COT report (Commitments of Traders Report). The COT holds a register of all open positions that are open to persons and entities required to report to the CFTC. The COT report aims to improve transparency in the futures market. Transparency is to reduce the information asymmetry in the derivatives market. The report is published on the cftc.gov website. Access to it is free. The report is released every Friday night at 21:30 PM (15:30 PM EST) and includes data for Tuesday (same week).
COT-type reports have a long history in the United States. Back in the 20s, the GFA (Grain Futures Administration) presented an annual report on activity on the futures market. From 1962, reports were published monthly. In the 90's the frequency of reports increased to 2-week intervals. In the XNUMXst century, reports are already being published every week.
COT reports are helpful for both private and professional traders in determining the market situation. Thanks to COT reports, the investor can find out what positions are predominant in large players and what is the direction of changes.
The report contains information on all long and short positions. Reported items are grouped by items entered by investors classified as commercials and Non-commercials. A separate category are non-reportable positions. The items reported to the COT usually cover from 70% -90% of the entire regulated market.
Data classified as not commercial they most often include speculative investors. These include, but are not limited to, hedge funds, retail investors and financial institutions. For example, a hedge fund may believe that gold will rise and therefore open a long position in a futures contract.
Data classified as commercial consist of positions that use futures contracts to hedge against the risk of unfavorable changes in the exchange rate or commodity prices. An example is a gold mining company that takes a short position in a gold futures contract to hedge against an adverse movement in the price of a precious metal. In summary, commercial positions are usually not entered into for purely speculative purposes.
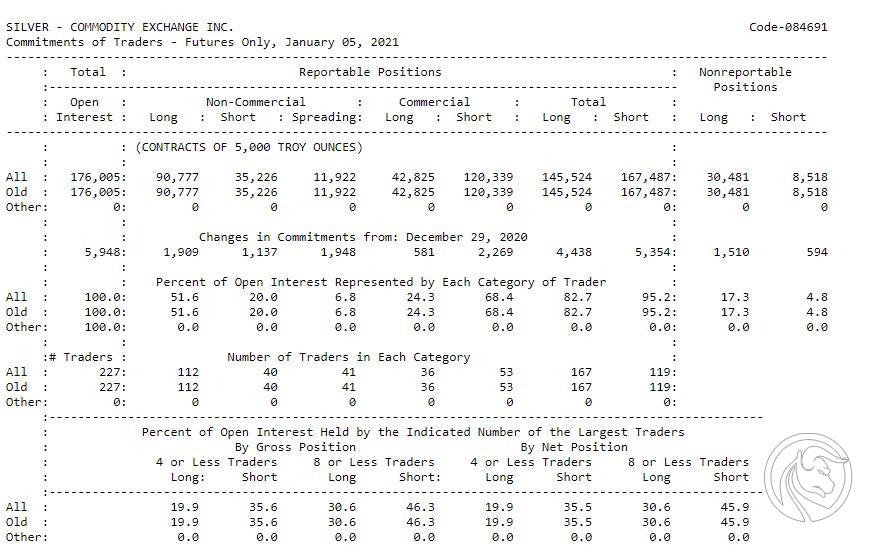
An excerpt from the COT report from January 5, 2020 on the situation on the silver futures market is presented below.
The above report shows that only 4,8% of all short positions were not included by entities obliged to submit reports to the COT. It can also be seen that non-commercial investors so far prefer long positions (90). There are definitely fewer short positions (777).
Summation
The operation of the CFTC is aimed at increasing transparency in the derivatives market. Publication of COT reports helps retail investors see the positions held by larger players. At the same time, the CFTC penalizes the use of unfair practices by participants in the derivative market. A great example is the fine imposed on JP Morgan in the third quarter of 2020. Worried, however, that the CFTC was unable to "nip" spoofing in the bud. The procedure lasted for 8 years. On the other hand, the regulator's limited budgetary resources do not allow it to act on a grand scale.























![Trading View platform – solutions tailored to the needs of traders [Review] trading view review](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/trading-view-recenzja-184x120.jpg?v=1709558918)
![How to connect your FP Markets account to the Trading View platform [Guide] fp markets trading view](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/fp-markets-trading-view-184x120.jpg?v=1708677291)
![How to invest in ChatGPT and AI? Stocks and ETFs [Guide] how to invest in chatgpt and artificial intelligence](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/jak-inwestowac-w-chatgpt-i-sztuczna-inteligencje-184x120.jpg?v=1676364263)


![WeWork – the anatomy of the collapse of a company valued at $47 billion [WeWork, part II] wework bankruptcy story](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/wework-bankructwo-historia-184x120.jpg?v=1711729561)
![Adam Neumann – the man who screwed up Softbank [WeWork, part AND] adam neumann wework](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/adam-neumann-wework-184x120.jpg?v=1711728724)





![How to transfer shares to another brokerage office [Procedure description] how to transfer shares to another brokerage house](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/jak-przeniesc-akcje-do-innego-biura-maklerskiego-184x120.jpg?v=1709556924)

![The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - The most common mistakes of a beginner trader - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Najczestsze-bledy-poczatkujacego-tradera-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1711601376)
![Learning patience: No position is also a position - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - Learning patience - No position is also a position - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Nauka-cierpliwosci-Brak-pozycji-to-tez-pozycja-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710999249)
![When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - Mr Yogi [VIDEO] Scalping - When to exit a position and how to minimize losses - VIDEO](https://forexclub.pl/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Scalping-Kiedy-wyjsc-z-pozycji-i-jak-minimalizowac-straty-VIDEO-184x120.jpg?v=1710336731)